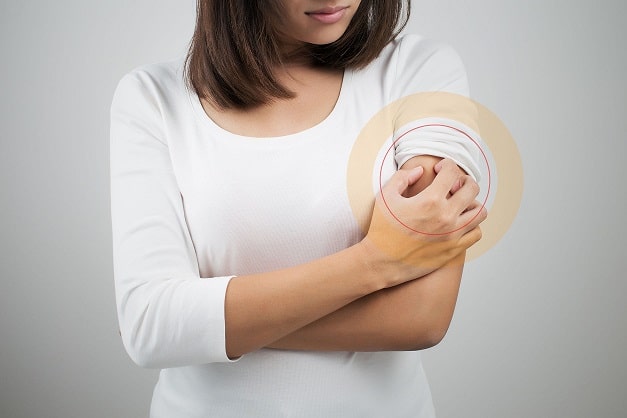


Commonly found on the skin, even in healthy people, Staphylococcus aureus or S.aureus is the most common bacteria involved in infections of the skin and wounds.3e
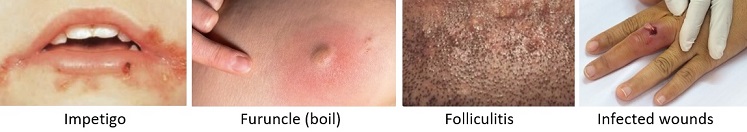
Treatment usually involves antibiotics and drainage of the infected area.10 Topical antibiotics can play an important role in the prevention and treatment of many bacterial skin infections.3
Topical antibiotic creams and ointments, such as fusidic acid or mupirocin can be prescribed or recommended over-the-counter for bacterial skin infections such as impetigo, infected cuts and grazes, and infected dermatitis. Topical antibiotics work by stopping the growth of the bacteria causing the infection. These topical creams can also be used to prevent wound infections from occurring.3 Sodium fusidate (available as an ointment) is a salt of fusidic acid and it works in the same way.11 Your doctor or pharmacist will be able to recommend the appropriate product to treat your infection.
In most cases, a bacterial skin infection does not cause serious harm. However, if left untreated, and the infection continues to penetrate even deeper it could enter the bloodstream, joints, bones, lungs or heart, and become dangerous.10



Disclaimer
This e-brochure has been auto-translated for your convenience. While machine translations are helpful, they may contain errors. Medinformer is actively working to have all translations reviewed by professional, mother-tongue language speakers, though this process will take time. For the most accurate information, please refer to the original English version. Medinformer and its partners cannot be held responsible for any inaccuracies that may result from the translation.
Thank you for your understanding.